A polyhistidine-tag is an amino acid motif in proteins that consists of at least five histidine (His) residues, often at the N- or C-terminus of the protein. It is also known as hexa histidine-tag, 6xHis-tag, and by the trademarked name His-tag. Polyhistidine-tags are often used for affinity purification of polyhistidine-tagged recombinant proteins expressed in Escherichia coli and other  prokaryotic expression systems.
prokaryotic expression systems.
Anti-His Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (5C3) was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen. This antibody has been tested with IF, IP and WB. Abbkine suggested starting dilutions are as follows: WB 1:3000, IP: 1:200, IF: 1:1000.
His tag is a short peptide composed of 6 histidine (His-His-His-His-His-His). Because its molecular weight is small, His tag is relatively easy to isolate and purify. I chose Anti-His Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (5C3) to detect the expression of His tag fusion protein. I am satisfied with the result.
 Glutathione S-transferase (GST) is a 26 kDa protein derived from Schistosoma japonicum. GST enzymes from various sources, both native and recombinantly expressed as fusion to the N-terminus of target proteins. Reduced glutathione (GSH), when immobilized as a ligand to agarose or other chromatography supports, enables high-yield and high-quality purification of recombinant proteins expressed as fusions with glutathione S-transferase (GST) or other glutathione binding proteins expressed in E. coli, insect cells and mammalian cells.
Glutathione S-transferase (GST) is a 26 kDa protein derived from Schistosoma japonicum. GST enzymes from various sources, both native and recombinantly expressed as fusion to the N-terminus of target proteins. Reduced glutathione (GSH), when immobilized as a ligand to agarose or other chromatography supports, enables high-yield and high-quality purification of recombinant proteins expressed as fusions with glutathione S-transferase (GST) or other glutathione binding proteins expressed in E. coli, insect cells and mammalian cells. Glutathione S-transferase (GST) is a 26 kDa protein derived from Schistosoma japonicum. GST enzymes from various sources, both native and recombinantly expressed as fusion to the N-terminus of target proteins, are easily purified using glutathione (GSH) agarose beads is well documented and provides a one-step, high purity affinity purification. Due to the positive influence of the GST-tag on protein solubility and expression efficiency especially of small proteins, this technique has been widely used to generate proteins for crystallization, molecular immunology studies and studies involving protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions.
Glutathione S-transferase (GST) is a 26 kDa protein derived from Schistosoma japonicum. GST enzymes from various sources, both native and recombinantly expressed as fusion to the N-terminus of target proteins, are easily purified using glutathione (GSH) agarose beads is well documented and provides a one-step, high purity affinity purification. Due to the positive influence of the GST-tag on protein solubility and expression efficiency especially of small proteins, this technique has been widely used to generate proteins for crystallization, molecular immunology studies and studies involving protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions. transfer. The HA tag antibody can specifically recognize the C terminal or N terminal with HA tag (HA-tagged) fusion protein, and also can be used to detect the HA expression of tag fusion protein expression, cellular localization, and purification, qualitative and quantitative detection of HA expression of tag fusion protein.
transfer. The HA tag antibody can specifically recognize the C terminal or N terminal with HA tag (HA-tagged) fusion protein, and also can be used to detect the HA expression of tag fusion protein expression, cellular localization, and purification, qualitative and quantitative detection of HA expression of tag fusion protein. well as for immunoaffinity purification of proteins expressed in cells. This antibody recognizes the GST-tag fused to either the amino- or carboxy-terminus of targeted proteins.
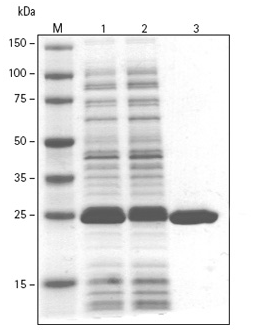
well as for immunoaffinity purification of proteins expressed in cells. This antibody recognizes the GST-tag fused to either the amino- or carboxy-terminus of targeted proteins. PurKine™ His-Tag Ni-Super Resin effectively purifies high levels of overexpressed His-tagged fusion proteins in gravity column procedures at a variety of scales. The Resin consists of 90μm beads of highly cross-linked 4% agarose, to which Nitilotriacetic acid (NTA) has been coupled. The chelating group has then been charged with nickel ions (Ni2+). Tests confirm that performance equals or exceeds popular Ni-NTA resins from other suppliers, and no decrease in performance occurs after at least five repeated uses.
PurKine™ His-Tag Ni-Super Resin effectively purifies high levels of overexpressed His-tagged fusion proteins in gravity column procedures at a variety of scales. The Resin consists of 90μm beads of highly cross-linked 4% agarose, to which Nitilotriacetic acid (NTA) has been coupled. The chelating group has then been charged with nickel ions (Ni2+). Tests confirm that performance equals or exceeds popular Ni-NTA resins from other suppliers, and no decrease in performance occurs after at least five repeated uses. generate its own fluorophore, the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria is used extensively as a fluorescent marker in molecular and cell biology.
generate its own fluorophore, the green fluorescent protein (GFP) from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria is used extensively as a fluorescent marker in molecular and cell biology.
 recognition by an antibody. If there is no antibody against a given protein, adding a FLAG-tag to a protein allows the protein to be studied with an antibody against the FLAG sequence. Examples are cellular localization studies by immunofluorescence or detection by SDS PAGE protein electrophoresis and Western blotting.
recognition by an antibody. If there is no antibody against a given protein, adding a FLAG-tag to a protein allows the protein to be studied with an antibody against the FLAG sequence. Examples are cellular localization studies by immunofluorescence or detection by SDS PAGE protein electrophoresis and Western blotting.
 Microtubules of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton perform essential and diverse functions and are composed of a heterodimer of alpha and beta tubulins. The genes encoding these microtubule constituents belong to the tubulin superfamily, which is composed of six distinct families. Genes from the alpha, beta and gamma tubulin families are found in all eukaryotes. The alpha and beta tubulins represent the major components of microtubules, while gamma tubulin plays a critical role in the nucleation of microtubule assembly. There are multiple alpha and beta tubulin genes, which are highly conserved among species.
Microtubules of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton perform essential and diverse functions and are composed of a heterodimer of alpha and beta tubulins. The genes encoding these microtubule constituents belong to the tubulin superfamily, which is composed of six distinct families. Genes from the alpha, beta and gamma tubulin families are found in all eukaryotes. The alpha and beta tubulins represent the major components of microtubules, while gamma tubulin plays a critical role in the nucleation of microtubule assembly. There are multiple alpha and beta tubulin genes, which are highly conserved among species. Tubulin is one of several members of a small family of globular proteins. The most common members of the tubulin family are α-tubulin and β-tubulin, the proteins that make up microtubules. Each has a molecular weight of approximately 55 kDa. Antibodies against β-Tubulin are useful as loading controls for Western Blotting. However it should be noted that levels of β-Tubulin may not be stable in certain cells, such as adipose tissue.
Tubulin is one of several members of a small family of globular proteins. The most common members of the tubulin family are α-tubulin and β-tubulin, the proteins that make up microtubules. Each has a molecular weight of approximately 55 kDa. Antibodies against β-Tubulin are useful as loading controls for Western Blotting. However it should be noted that levels of β-Tubulin may not be stable in certain cells, such as adipose tissue.
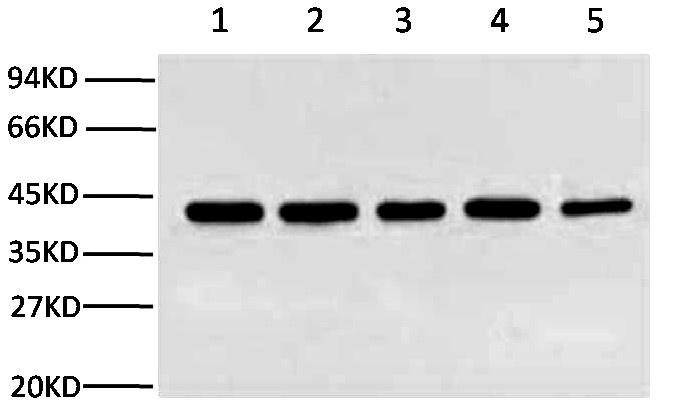 Beta-actin is an isform of actin proteins. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility, structure, and integrity. Beta-actin, also known as a "housekeeping" protein, is usually used as a loading control, for among others, the integrity of cells, protein degradation, in PCR and Western blotting. Loading controls are essential for proper interpretation of western blots. They can be used to normalize the levels of protein detected by confirming that protein loading is the same across the gel.
Beta-actin is an isform of actin proteins. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in cell motility, structure, and integrity. Beta-actin, also known as a "housekeeping" protein, is usually used as a loading control, for among others, the integrity of cells, protein degradation, in PCR and Western blotting. Loading controls are essential for proper interpretation of western blots. They can be used to normalize the levels of protein detected by confirming that protein loading is the same across the gel. polymerase II. TBP is involved in DNA melting (double strand separation) by bending the DNA by 80° (the AT-rich sequence to which it binds facilitates easy melting). The TBP is an unusual protein in that it binds the minor groove using a β sheet. Another distinctive feature of TBP is a long string of glutamines in the N-terminus of the protein. This region modulates the DNA binding activity of the C-terminus, and modulation of DNA-binding affects the rate of transcription complex formation and initiation of transcription. Mutations that expand the number of CAG repeats encoding this polyglutamine tract, and thus increase the length of the polyglutamine string, are associated with spinocerebellar ataxia 17, a neurodegenerative disorder classified as a polyglutamine disease.
polymerase II. TBP is involved in DNA melting (double strand separation) by bending the DNA by 80° (the AT-rich sequence to which it binds facilitates easy melting). The TBP is an unusual protein in that it binds the minor groove using a β sheet. Another distinctive feature of TBP is a long string of glutamines in the N-terminus of the protein. This region modulates the DNA binding activity of the C-terminus, and modulation of DNA-binding affects the rate of transcription complex formation and initiation of transcription. Mutations that expand the number of CAG repeats encoding this polyglutamine tract, and thus increase the length of the polyglutamine string, are associated with spinocerebellar ataxia 17, a neurodegenerative disorder classified as a polyglutamine disease. Anti-Cyclophilin B Monoclonal Antibody(7B2)
Anti-Cyclophilin B Monoclonal Antibody(7B2) Anti-Lamin B1 Monoclonal Antibody(15T1) was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen, with reactivity including Human, Mouse and Rat. This antibody has been routinely tested with WB and IP applications. And Abbkine suggested starting dilutions are as follows: WB 1:2000-5000, IP 1:200.
Anti-Lamin B1 Monoclonal Antibody(15T1) was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using specific immunogen, with reactivity including Human, Mouse and Rat. This antibody has been routinely tested with WB and IP applications. And Abbkine suggested starting dilutions are as follows: WB 1:2000-5000, IP 1:200. Loading controls are usually proteins that exhibit high-level, constitutive expression in the cell type or sample you are examining. This ensures constant expression levels. Thus "housekeeping genes" are frequently chosen for use as loading controls. It is also important that the protein chosen as a loading control has a different molecular weight with the protein of interest so that the bands are distinct and expression levels quantifiable. The most popular loading control detection antibody for Nucleoprotein is Anti-Histone H3 antibody. Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes and the histone gene is highly conserved.
Loading controls are usually proteins that exhibit high-level, constitutive expression in the cell type or sample you are examining. This ensures constant expression levels. Thus "housekeeping genes" are frequently chosen for use as loading controls. It is also important that the protein chosen as a loading control has a different molecular weight with the protein of interest so that the bands are distinct and expression levels quantifiable. The most popular loading control detection antibody for Nucleoprotein is Anti-Histone H3 antibody. Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes and the histone gene is highly conserved.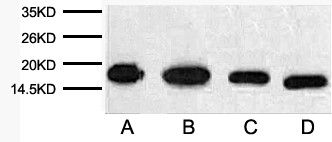 Histone H3 is one of the five main histone proteins involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability.
Histone H3 is one of the five main histone proteins involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. molecule, converting molecular oxygen to two molecules of water.
molecule, converting molecular oxygen to two molecules of water.
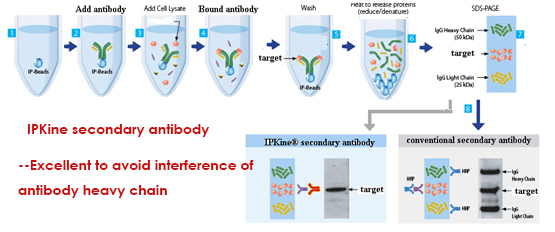
 in immunoprecipitation (IP)or co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP): the primary antibody they use in IP or co-IP is the same as the one they have used in WB, or they raised from the same host. When this happens, the secondary antibody will recognize the primary antibody used in WB as well as the denatured/reduced primary antibody released during the IP procedure . It directly result in two bands: the heavy chain (50kDa) and the light chain (25kDa).
in immunoprecipitation (IP)or co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP): the primary antibody they use in IP or co-IP is the same as the one they have used in WB, or they raised from the same host. When this happens, the secondary antibody will recognize the primary antibody used in WB as well as the denatured/reduced primary antibody released during the IP procedure . It directly result in two bands: the heavy chain (50kDa) and the light chain (25kDa).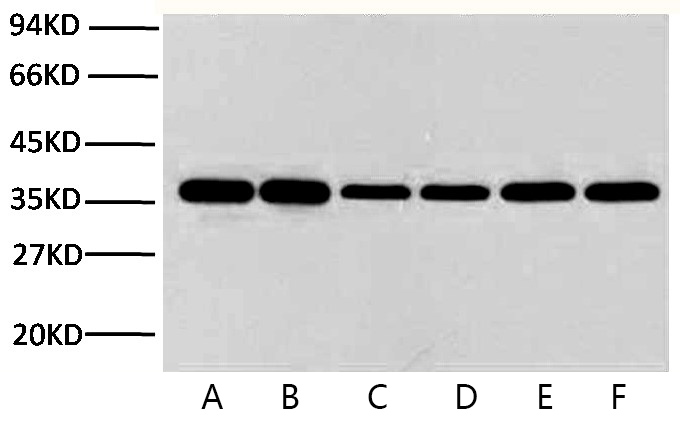 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (abbreviated as GAPDH or less commonly as G3PDH) is an enzyme of ~37kDa that catalyzes the sixth step of glycolysis and thus serves to break down glucose for energy and carbon molecules. In addition to this long established metabolic function, GAPDH has recently been implicated in several non-metabolic processes, including transcription activation, initiation of apoptosis ER to Golgi vesicle shuttling, and fast axonal, or axoplasmic transport.
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (abbreviated as GAPDH or less commonly as G3PDH) is an enzyme of ~37kDa that catalyzes the sixth step of glycolysis and thus serves to break down glucose for energy and carbon molecules. In addition to this long established metabolic function, GAPDH has recently been implicated in several non-metabolic processes, including transcription activation, initiation of apoptosis ER to Golgi vesicle shuttling, and fast axonal, or axoplasmic transport.