Since
Abbkine document collection began, as of December 31, 2019, the number of
English articles published by google using Abbkine products has exceeded 1400,
with an impact factor exceeding 5400 points.
Thank you
for your trust and support to Abbkine. We will continuously stimulate our
internal creativity, provide competitive biomedical products and services, and
continuously create maximum value for our customers. With a view to becoming a
respected and world-class provider of biomedical products and services.
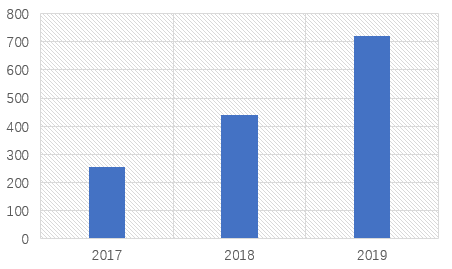
Figure 1:
Number of English Articles Published Using Abbkine Products from 2017 to 2019
In December 2019, Abbkine added 200+ citations. Some high-score citations are as below.
- LECT2,
a Ligand for Tie1, Plays a Crucial Role in Liver Fibrogenesis.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.021
Magazine:
Cell
Impact: 24.38
Abstract:
Liver
fibrosis is a very common condition seen in millions of patients with various
liver diseases, and yet no effective treatments are available owing to poorly
characterized molecular pathogenesis. Here, we show that leukocyte cell-derived
chemotaxin 2 (LECT2) is a functional ligand of Tie1, a poorly characterized
endothelial cell (EC)-specific orphan receptor. Upon binding to Tie1, LECT2
interrupts Tie1/Tie2 heterodimerization, facilitates Tie2/Tie2
homodimerization, activates PPAR signaling, and inhibits the migration and tube
formations of EC. In vivo studies showed that LECT2 overexpression inhibits
portal angiogenesis, promotes sinusoid capillarization, and worsens fibrosis,
whereas these changes were reversed in Lect2-KO mice. Adeno-associated viral vector
serotype 9 (AAV9)-LECT2 small hairpin RNA (shRNA) treatment significantly
attenuates fibrosis. Upregulation of LECT2 is associated with advanced human
liver fibrosis staging. We concluded that targeting LECT2/Tie1 signaling may
represent a potential therapeutic target for liver fibrosis, and serum LECT2
level may be a potential biomarker for the screening and diagnosis of liver
fibrosis.
Products
using from Abbkine:
IPKine™ HRP, Goat Anti-Mouse IgG HCS
(CAT#: A25112)
IPKine™ HRP, Goat Anti-Mouse IgG LCS (CAT#: A25012)
2. EMS1 and BRI1 control separate biological processes via extracellular domain diversity and intracellular domain conservation.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-12112-w
Magazine: Nature
Communications volume
Impact: 12.19
Abstract: In
flowering plants, EMS1 (Excess Microsporocytes 1) perceives TPD1 (Tapetum
Determinant 1) to specify tapeta, the last somatic cell layer nurturing pollen
development. However, the signaling components downstream of EMS1 are
relatively unknown. Here, we use a molecular complementation approach to
investigate the downstream components in EMS1 signaling. We show that the EMS1
intracellular domain is functionally interchangeable with that of the
brassinosteroid receptor BRI1 (Brassinosteroid Insensitive 1). Furthermore,
expressing EMS1 together with TPD1 in the BRI1 expression domain could
partially rescue bri1 phenotypes, and led to the dephosphorylation of BES1, a
hallmark of active BRI1 signaling. Conversely, expressing BRI1 in the EMS1
expression domain could partially rescue ems1 phenotypes. We further show that
PpEMS1 and PpTPD1 from the early land plant Physcomitrella patens could
completely rescue ems1 and tpd1 phenotypes, respectively. We propose that EMS1 and
BRI1 have evolved distinct extracellular domains to control different
biological processes but can act via a common intracellular signaling pathway.
Products using from Abbkine:
Anti-Plant Actin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (3T3) (CAT#: A01050)
3. PLK4 deubiquitination by Spata2‐CYLD suppresses NEK7‐mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation at the centrosome.
https://www.embopress.org/doi/abs/10.15252/embj.2019102201
Magazine: EMBO
JOURNAL
Impact: 10.55
Abstract:
The innate
immune sensor NLRP3 assembles an inflammasome complex with NEK7 and ASC to
activate caspase‐1 and drive the maturation of proinflammatory cytokines IL‐1β
and IL‐18. NLRP3 inflammasome activity must be tightly controlled, as its
over‐activation is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Here,
we show that NLRP3 inflammasome activation is suppressed by a centrosomal
protein Spata2. Spata2 deficiency enhances NLRP3 inflammasome activity both in
the macrophages and in an animal model of peritonitis. Mechanistically, Spata2
recruits the deubiquitinase CYLD to the centrosome for deubiquitination of
polo‐like kinase 4 (PLK4), the master regulator of centrosome duplication.
Deubiquitination of PLK4 facilitates its binding to and phosphorylation of NEK7
at Ser204. NEK7 phosphorylation in turn attenuates NEK7 and NLRP3 interaction,
which is required for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Pharmacological or
shRNA‐mediated inhibition of PLK4, or mutation of the NEK7 Ser204
phosphorylation site, augments NEK7 interaction with NLRP3 and causes increased
NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Our study unravels a novel centrosomal
regulatory pathway of inflammasome activation and may provide new therapeutic
targets for the treatment of NLRP3‐associated inflammatory diseases.
Products using from Abbkine:
IFKine™ Green Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG (CAT#: A24211)
4. Cross-Microbial Protection via Priming a Conserved Immune Co-Receptor through Juxtamembrane Phosphorylation in Plants
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2019.10.010
Magazine: Cell
Host & Microbe
Impact: 10.5
Abstract: Living
organisms can be primed for potentiated responses to recurring stresses based
on prior experience. However, the molecular basis of immune priming remains
elusive in plants that lack adaptive immunity. Here, we report that bacterial
challenges can prepare plants for fungal attacks by inducing juxtamembrane
phosphorylation of CERK1, the co-receptor indispensable for signaling in
response to the fungal elicitor chitin. This phosphorylation is mediated by
BAK1, a co-receptor for signaling in response to multiple elicitors. BAK1
interacts with CERK1, and loss of BAK1 reduces priming phosphorylation of
CERK1. Juxtamembrane phosphomimetic mutations of CERK1 confer accelerated
chitin responses and fortified fungal resistance without triggering
constitutive immunity, whereas juxtamembrane phosphodeficient mutations
diminish bacteria-induced protection against fungal infection. These findings
reveal that crosstalk between cell-surface immune co-receptors can prime
defense and demonstrate that juxtamembrane phosphorylation of plant
receptor-like kinases can occur independent of kinase activation to place the
protein into a prime state.
Products using from Abbkine:
Anti-GST Tag Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (2A8) (CAT#: A02030)
5. Extracellular vesicles of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts creates a pre-metastatic niche in the lung through activating fibroblasts
https://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12943-019-1101-4
Magazine: Molecular
Cancer
Impact: 9.17
Abstract: Carcinoma-associated
fibroblasts (CAFs) have been known to promote cancer progression by modifying
the primary tumor microenvironment. We aimed to elucidate the intercellular
communication between CAFs and secondary organs in salivary adenoid cystic
carcinoma (SACC) metastasis.
Products using from Abbkine:
FITC, Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (CAT#: A22120)
Dylight 488, Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG
(CAT#: A23220)
Dylight 549, Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG
(CAT#: A23320)
Please learn more
details from https://www.abbkine.com/publications/ .
没有评论:
发表评论