In April 2020, Abbkine collected 210 English
articles published using Abbkine products, and some of them sent us good news
on their own initiative. The joy was beyond words. In this collection of
articles, the highest impact factor (IF) is 13.05, with articles with IF>7
accounting for 10.4% and articles with IF>4 accounting for 43%.
In the current evaluation of scientific
research, scientific research papers, as the systematic summary and theoretical
crystallization of scientific research carried out by scientific researchers,
are still the main objects for measuring innovative activities, especially
basic research activities. Science, Nature and Cell are internationally
recognized journals with the highest academic reputation. According to the
statistical results of Chinese scientific papers in 2018, the number of Chinese
papers published in the above three journals in 2017 was 309, an increase of 11
articles over the previous year, ranking fourth in the world. China's
scientific research strength should not be underestimated!
Let's take a look at some of the research
workers in China who are studying some topics.
Title: MST4 kinase suppresses
gastric tumorigenesis by limiting YAP activation via a non-canonical pathway
Magazine: Journal of
Experimental Medicine
Impact
factor:
9.83
University:
Tongji University
Abstract: Hyperactivation of YAP has been commonly associated with tumorigenesis,
and emerging evidence hints at multilayered Hippo-independent regulations of
YAP. In this study, we identified a new MST4–YAP
axis, which acts as a noncanonical Hippo signaling pathway that limits
stress-induced YAP activation. MST4 kinase directly phosphorylated YAP at Thr83
to block its binding with importin α, therefore leading to YAP cytoplasmic
retention and inactivation. Due to a consequential interplay between
MST4-mediated YAP phospho-Thr83 signaling and the classical YAP phospho-Ser127
signaling, the phosphorylation level of YAP at Thr83 was correlated to that at
Ser127. Mutation of T83E mimicking MST4-mediated alternative signaling
restrained the activity of both wild-type YAP and its S127A mutant mimicking
loss of classical Hippo signal. Depletion of MST4 in mice promoted gastric
tumorigenesis with diminished Thr83 phosphorylation and hyperactivation of YAP.
Moreover, loss of MST4–YAP signaling was associated with poor
prognosis of human gastric cancer. Collectively, our study uncovered a
noncanonical MST4–YAP signaling axis essential for suppressing
gastric tumorigenesis.
Article link: https://rupress.org/jem/article/217/6/e20191817/151647
Products
using from Abbkine:
IPKine™ HRP, Goat Anti-Mouse
IgG LCS (CAT#A25012)
IPKine™
HRP, Mouse Anti-Rabbit IgG LCS (CAT#A25022)


Title:
TRIM32/USP11
Balances ARID1A Stability and the Oncogenic/Tumor-Suppressive Status of
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Magazine: Cell Reports
Impact
factor:
8.04
University:
Chinese
Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College
Abstract: Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is an
aggressive epithelial malignancy, yet the molecular mechanisms underlying SCC
development are elusive. ARID1A is frequently mutated in various cancer types,
but both mutation rates and expression levels of ARID1A are ubiquitously low in
SCCs. Here, we reveal that excessive protein degradation mediated by the
ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) contributes to the loss of ARID1A expression
in SCC. We identify that the E3 ligase TRIM32 and the deubiquitinase USP11 play
key roles in controlling ARID1A stability. TRIM32 depletion inhibits SCC cell
proliferation, metastasis, and chemoresistance by stabilizing ARID1A, while
USP11 depletion promotes SCC development by promoting ARID1A degradation. We
show that syndecan-2 (SDC2) is the downstream target of both ARID1A and USP11
and that SDC2 depletion abolishes the oncogenic function of ARID1A loss. In
summary, our data reveal UPS-mediated protein degradation as a mechanism
underlying ARID1A loss and propose an important role for the
TRIM32/USP11-ARID1A-SDC2 axis in SCC.
Article link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124719316675
Products
using from Abbkine:
ExKineTM
Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction Kit (CAT#KTP3001)

Title:
Microneedle
drug eluting balloon for enhanced drug delivery to vascular tissue
Magazine:
Journal
of Controlled Release
Impact
factor: 7.82
University:
Yonsei
University, Seoul
Abstract: High rates of restenosis and neointimal
formation have driven increasing interest in the application of drug eluting
balloons (DEB) as counteractive measures for intraluminal drug delivery. The
use of DEBs eliminates the need for stents so that serious side effects including
in-stent restenosis and stent thrombosis can be avoided and long-term
medication of antiplatelet agent is not needed. Despite their benefits, DEBs
have poor drug delivery efficiency due to short balloon inflation times (30~60
seconds) that limit the passive drug diffusion from the balloon surface to the
luminal lesion. To increase drug delivery efficiency, a microneedle DEB (MNDEB)
was developed by a conformal transfer molding process using a thin polydimethylsiloxane
mold bearing a negative array of MNs of 200 μm in height. A MN
array composed of UV curable resin was formed onto the surface of DEB, and
drugs were coated onto the structure. The mechanical properties of the MN array
were investigated and MN
penetration
into luminal vasculature was confirmed in vivo. An increase in drug delivery efficiency
compared to a standard DEB was demonstrated in an in vivo test in a rabbit
aorta. Finally, the superior therapeutic efficacy of MNDEBs was evaluated using
an atherosclerosis rabbit model.
Article link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168365920300894
Products
using from Abbkine:
EliKine™
Mouse IL-1β
ELISA Kit (CAT#KET7005)
EliKine™
Mouse TNF-α
ELISA Kit (CAT#KET7015)


Title:
Polyphyllin
VI Induces Caspase-1-Mediated Pyroptosis via the Induction of ROS/NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD
Signal Axis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Magazine:
Cancers
Impact
factor: 5.87
University:
Southwest
Medical University
Abstract: Trillium tschonoskii Maxim
(TTM), a traditional Chinese medicine, has been demonstrated to have a potent
anti-tumor effect. Recently, polyphyllin VI (PPVI), a main saponin isolated
from TTM, was reported by us to significantly suppress the proliferation of
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) via the induction of apoptosis and autophagy
in vitro and in vivo. In this study, we further found that the NLRP3
inflammasome was activated in PPVI administrated A549-bearing athymic nude
mice. As is known to us, pyroptosis is an inflammatory form of
caspase-1-dependent programmed cell death that plays an important role in
cancer. By using A549 and H1299 cells, the in vitro effect and action mechanism
by which PPVI induces activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in NSCLC were
investigated. The anti-proliferative effect of PPVI in A549 and H1299 cells was
firstly measured and validated by MTT assay. The activation of the NLRP3
inflammasome was detected by using Hoechst33324/PI staining, flow cytometry
analysis and real-time live cell imaging methods. We found that PPVI
significantly increased the percentage of cells with PI signal in A549 and
H1299, and the dynamic change in cell morphology and the process of cell death
of A549 cells indicated that PPVI induced an apoptosis-to-pyroptosis switch,
and, ultimately, lytic cell death. In addition, belnacasan (VX-765), an
inhibitor of caspase-1, could remarkably decrease the pyroptotic cell death of
PPVI-treated A549 and H1299 cells. Moreover, by detecting the expression of
NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1, IL-1β, IL-18 and GSDMD in A549 and h1299 cells using Western
blotting, immunofluorescence imaging and flow cytometric analysis, measuring
the caspase-1 activity using colorimetric assay, and quantifying the cytokines
level of IL-1β and
IL-18 using ELISA, the NLRP3 inflammasome was found to be activated in a dose
manner, while VX-765 and necrosulfonamide (NSA), an inhibitor of GSDMD, could
inhibit PPVI-induced activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Furthermore, the
mechanism study found that PPVI could activate the NF-κB signaling pathway via increasing reactive
oxygen species (ROS) levels in A549 and H1299 cells, and N-acetyl-L-cysteine
(NAC), a scavenger of ROS, remarkably inhibited the cell death, and the
activation of NF-κB and the NLRP3 inflammasome in PPVI-treated A549 and H1299
cells. Taken together, these data suggested that PPVI-induced,
caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis via the induction of the ROS/NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD
signal axis in NSCLC, which further clarified the mechanism of PPVI in the
inhibition of NSCLC, and thereby provided a possibility for PPVI to serve as a
novel therapeutic agent for NSCLC in the future
Article link: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/12/1/193
Products
using from Abbkine:
Caspase-1
Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (CAT#KTA3020)

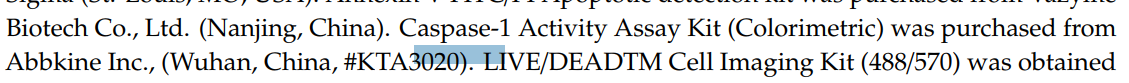
Title:
Integrin
β3 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation
and attenuates hypoxia-induced apoptosis via regulating the PTEN/Akt/mTOR and
ERK1/2 pathways
Magazine: International
Journal of Biological Sciences
Impact
factor:
4.04
University:
Shanghai
Jiaotong University
Article link: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6990915/
Abstract: Integrin β3 is one
of the main integrin heterodimer receptors on the surface of cardiac myocytes.
Our previous studies showed that hypoxia induces apoptosis and increases
integrin β3
expression in cardiomyocytes. However, the exact mechanism by which integrin β3 protects
against apoptosis remains unclear. Hence, the present investigation aimed to
explore the mechanism of integrin β3 in cardiomyocyte proliferation and
hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Products
using from Abbkine:
Annexin V-AbFluor™ 555 Apoptosis Detection kit (CAT#KTA0003)

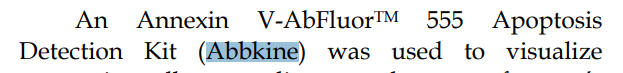
没有评论:
发表评论