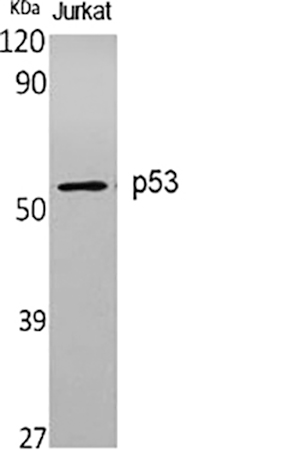
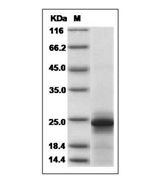
P53 gene, human tumor suppressor gene. The gene encodes a protein with a molecular weight of 43.7KDa, but is named P53 because the protein band appears at 53KDa shown by Marker. Wild-type p53 causes cancer cells to apoptosis, thus preventing canceration; But also has the function of helping cell genes repair defects; Studies have found that mutant p53 can enhance canceration. 50% of human tumors are related to P53 gene. Currently, there are liver cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, gastric cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, ovarian cancer, brain tumor, lymphocyte tumor, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, osteosarcoma, etc. P53 mutation in human tumors is mainly in highly conserved regions, with the highest mutation at 175, 248, 249, 273, 282 sites, and different types of tumors.
P53 has a very short half-life, so it is almost undetectable in unstressed cells. This is mainly realized by the continuous ubiquitination of p53 and the degradation of 26S proteasome in the later stage under the action of its inhibitor MDM2. Cell stress signals such as DNA damage can inhibit ubiquitination of p53 and lead to its stabilization and activation. Once p53 is activated, it will bind to its downstream target regulatory elements and regulate its transcription. Therefore, various cell therapy schemes based on different tumor inhibition functions of p53 can be started. Just because past studies have shown that p53 gene mutations exist in about half of cancers, scientists regard them as important targets for developing new cancer therapies.
Abbkine P53 Antibody Helps Basic Cancer
Research! Basic information about the product:
| Product name | #CAT | Reactivity | Applications | Dilution ratio |
| p53 Polyclonal Antibody | ABP0110 | Human, Monkey, Mouse, Rat | WB/IF/IHC-P/ELISA | WB (1:500-1:2000) IF (1:200-1:1000) IHC-P (1:100-1:300) ELISA (1:10000). |
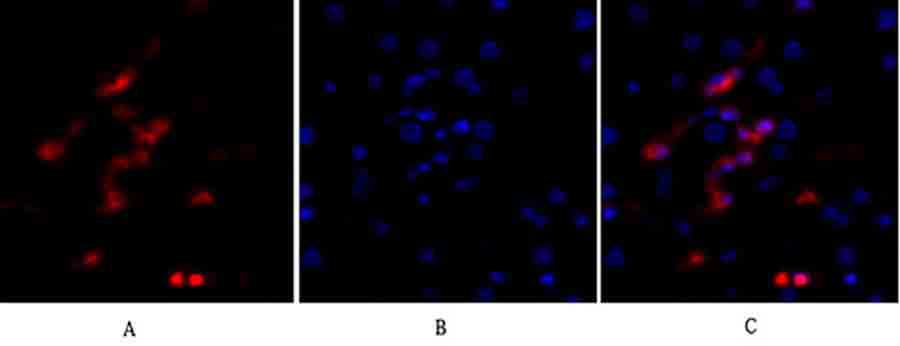
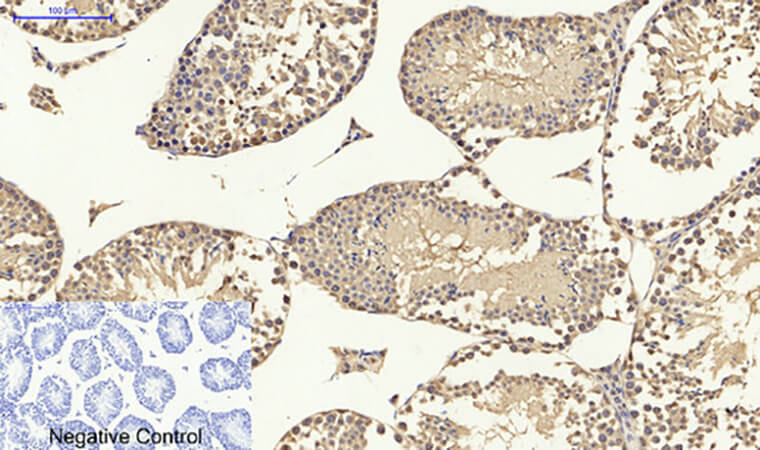
Abbkine P53 Antibody verification results: